| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 2.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2009-06-23 21:03:08 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:24:49 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | T3D1881 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Silver(I) hexafluoroantimonate |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | Silver(I) hexafluoroantimonate is a chemical compound of antimony and silver. Antimony is a metallic element with the chemical symbol Sb and atomic number 51. Small amounts of antimony are found in the earth's crust. Silver is a metallic element with the chemical symbol Ag and atomic number 47. It occurs naturally in its pure, free form, as an alloy with gold and other metals, and in minerals such as argentite and chlorargyrite. (12, 10, 11) |
|---|
| Compound Type | - Antimony Compound
- Fluoride Compound
- Food Toxin
- Inorganic Compound
- Pollutant
- Silver Compound
- Synthetic Compound
|
|---|
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | | Silver hexafluoroantimonate | | Silver hexafluoroantimonate(1-) | | Silver(I) hexafluoroantimonic acid |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | AgH6O6Sb |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 331.670 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 329.825 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 26042-64-8 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | silver(1+) ion hexahydroxystibanuide |
|---|
| Traditional Name | silver(1+) ion hexahydroxystibanuide |
|---|
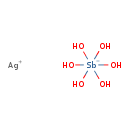
| SMILES | [Ag+].O[Sb-](O)(O)(O)(O)O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/Ag.6H2O.Sb/h;6*1H2;/q+1;;;;;;;+5/p-6 |
|---|
| InChI Key | InChIKey=JLMJIZQYMCLWJK-UHFFFAOYSA-H |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of inorganic compounds known as miscellaneous mixed metal/non-metals. These are inorganic compounds containing non-metal as well as metal atoms but not belonging to afore mentioned classes. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Inorganic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Mixed metal/non-metal compounds |
|---|
| Class | Miscellaneous mixed metal/non-metals |
|---|
| Sub Class | Not Available |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Miscellaneous mixed metal/non-metals |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Inorganic silver salt
- Inorganic salt
- Miscellaneous mixed metal/non-metal
- Inorganic metalloid salt
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Not Available |
|---|
| External Descriptors | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Exogenous |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | Not Available |
|---|
| Applications | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Appearance | White powder. |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | | Solubility | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | View |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-000i-0009000000-c60e9fcaeaaeb0aff72d | 2016-06-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-000i-0009000000-c60e9fcaeaaeb0aff72d | 2016-06-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-000i-0009000000-c60e9fcaeaaeb0aff72d | 2016-06-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-000i-0009000000-64b2380a13f9996c6a29 | 2016-08-04 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-000i-0009000000-64b2380a13f9996c6a29 | 2016-08-04 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-000i-0009000000-64b2380a13f9996c6a29 | 2016-08-04 | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Inhalation (10) ; oral (10) ; dermal (10) |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | The inhalation data suggests that the myocardium is a target of antimony toxicity. It is possible that antimony affects circulating glucose by interfering with enzymes of the glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis pathways. The mechanism of action of antimony remains unclear. However, some studies suggest that antimony combines with sulfhydryl groups including those in several enzymes important for tissue respiration. The antidotal action of BAL depends on its ability to prevent or break the union between antimony and vital enzymes. Moreover, the The cause of death is believed to be essentially the same as that in acute arsenic poisoning. Metallic silver is oxidized and may deposit in the tissues, causing arygria. The silver ion is known to inhibit glutathione peroxidase and NA+,K+-ATPase activity, disrupting selenium-catalyzed sulfhydryl oxidation-reduction reactions and intracellular ion concentrations, respectively. Silver nanoparticles are believed to disrupt the mitochondrial respiratory chain, causing oxidative stress, reduced ATP synthesis, and DNA damage. (11, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 10, 1) |
|---|
| Metabolism | Antimony is widely distributed throughout the body. The hair and skin contain the highest levels of antimony. The adrenal glands, lung, large intestine, trachea, cerebellum, and kidneys also contain relatively high levels of antimony. Blood is the main vehicle for the transport of absorbed antimony to various tissue compartments of the body. Antimony is a metal and, therefore, does not undergo catabolism. Antimony can covalently interact with sulfhydryl groups and phosphate, as well as numerous reversible binding interactions with endogenous ligands (e.g., proteins). It is not known if these interactions are toxicologically significant. Antimony is excreted via the urine and feces. Some of the fecal antimony may represent unabsorbed antimony that is cleared from the lung via mucociliary action into the esophagus to the gastrointestinal tract. Silver and its compounds can be absorbed via inhalation, while silver compounds can also be absorbed orally and dermally. It distributes throughout the body in the blood, particularily to the liver. Insoluble silver salts are transformed into soluble silver sulfide albuminates, bind to amino or carboxyl groups in RNA, DNA, and proteins, or are reduced to metallic silver by ascorbic acid or catecholamines. Metallic silver is oxidized and may deposit in the tissues, causing arygria. Silver is eliminated primarily in the faeces. (11, 10) |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | Not Available |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity (not listed by IARC). (9) |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | Breathing air, drinking water, and eating foods that contain antimony. Exposure can also occur through dermal or skin contact (10). |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | Dermal exposure to antimony can cause antimony spots (papules and pustules around sweat and sebaceous glands). Antimony poisoning can also lead to pneumoconiosis. Alterations in pulmonary function and other effects including chronic bronchitis, chronic emphysema, inactive tuberculosis, pleural adhesions, and irritation can result from inhalation of antimony. Increased blood pressure can also result from antimony poisoning. Myocardial depression, vasodilation and fluid loss may cause shock with hypotension, electrolyte disturbances and acute renal failure. Cerebral oedema, coma, convulsions, and death are possible. Exposure to high levels of silver for a long period of time may result in a condition called arygria, a blue-gray discoloration of the skin and other body tissues. Argyria is a permanent effect but does not appear to be harmful to health. While silver itself is not toxic, most silver salts are, and may damage the liver, kidney, and central nervous system, as well as be carcinogenic. (11, 12, 13, 10) |
|---|
| Symptoms | Abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea can result from inhalation of antimony. Dyspnea, headache, vomiting,cough, conjunctivitis, and bloody purulent discharge from nose can result from inhalation exposure. Skin or eye contact can cause pain and redness of the exposed surface. Exposure to high levels of silver for a long period of time may result in a condition called arygria, a blue-gray discoloration of the skin and other body tissues. Argyria is a permanent effect but does not appear to be harmful to health. Exposure to high levels of silver in the air has resulted in breathing problems, lung and throat irritation, and stomach pains. Skin contact with silver can cause mild allergic reactions such as rash, swelling, and inflammation in some people. (11, 8, 10) |
|---|
| Treatment | Following oral exposure to antimony, administer charcoal as a slurry (240 mL water/30 g charcoal). Following inhalation exposure, move patient to fresh air. Monitor for respiratory distress. If cough or difficulty breathing develops, evaluate for respiratory tract irritation, bronchitis, or pneumonitis. Administer oxygen and assist ventilation as required. Treat bronchospasm with inhaled beta2 agonist and oral or parenteral corticosteroids. In case of eye exposure, irrigate exposed eyes with copious amounts of room temperature water for at least 15 minutes. Following dermal exposure, Remove contaminated clothing and wash exposed area thoroughly with soap and water. A physician may need to examine the area if irritation or pain persists. (7) |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | Not Available |
|---|
| HMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 6337126 |
|---|
| ChEMBL ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChemSpider ID | 30780135 |
|---|
| KEGG ID | Not Available |
|---|
| UniProt ID | Not Available |
|---|
| OMIM ID | |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| CTD ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Stitch ID | Silver(I) hexafluoroantimonate |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ACToR ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| MSDS | T3D1881.pdf |
|---|
| General References | - Poon R, Chu I, Lecavalier P, Valli VE, Foster W, Gupta S, Thomas B: Effects of antimony on rats following 90-day exposure via drinking water. Food Chem Toxicol. 1998 Jan;36(1):21-35. [9487361 ]
- Bianchini A, Playle RC, Wood CM, Walsh PJ: Mechanism of acute silver toxicity in marine invertebrates. Aquat Toxicol. 2005 Mar 25;72(1-2):67-82. Epub 2004 Dec 29. [15748748 ]
- AshaRani PV, Low Kah Mun G, Hande MP, Valiyaveettil S: Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in human cells. ACS Nano. 2009 Feb 24;3(2):279-90. doi: 10.1021/nn800596w. [19236062 ]
- Kim S, Choi JE, Choi J, Chung KH, Park K, Yi J, Ryu DY: Oxidative stress-dependent toxicity of silver nanoparticles in human hepatoma cells. Toxicol In Vitro. 2009 Sep;23(6):1076-84. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2009.06.001. Epub 2009 Jun 7. [19508889 ]
- Dillard CJ, Tappel AL: Mercury, silver, and gold inhibition of selenium-accelerated cysteine oxidation. J Inorg Biochem. 1986 Sep;28(1):13-20. [3760861 ]
- Hayes WJ Jr. and Laws ER Jr. (eds) (1991). Handbook of Pesticide Toxicology. Volume 3. Classes of Pesticides. New York, NY: Academic Press, Inc.
- Rumack BH (2009). POISINDEX(R) Information System. Englewood, CO: Micromedex, Inc. CCIS Volume 141, edition expires Aug, 2009.
- Hamilton A and Hardy HL (1974). Industrial Toxicology. 3rd ed. Acton, MA: Publishing Sciences Group, Inc.
- International Agency for Research on Cancer (2014). IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. [Link]
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (1992). Toxicological profile for antimony. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (1990). Toxicological profile for silver. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- Wikipedia. Silver. Last updated Dec 2014. [Link]
- International Programme on Chemical Safety (IPCS) INCHEM (1977). WHO Food Additive Series No. 12: Silver. [Link]
|
|---|
| Gene Regulation |
|---|
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|