
Browsing Toxins By Category
| T3DB ID | Name CAS Number | Formula Weight | Structure | Type | Mechanism of Toxicity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T3D0001 | Arsenic 7440-38-2 | As 74.920 g/mol | 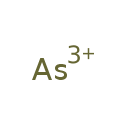 |
| Arsenic and its metabolites disrupt ATP production through several mechanisms. At the level of the citric acid cycle, arsenic inhibits pyruvate dehydrogenase and by co...more Number of Targets: 46 |
| T3D0002 | Lead 7439-92-1 | Pb 207.200 g/mol | 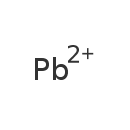 |
| Lead mimics other biologically important metals, such as zinc, calcium, and iron, competing as cofactors for many of their respective enzymatic reactions. For example,...more Number of Targets: 31 |
| T3D0003 | Mercury 7439-97-6 | Hg 200.590 g/mol |  |
| High-affinity binding of the divalent mercuric ion to thiol or sulfhydryl groups of proteins is believed to be the major mechanism for the activity of mercury. Through...more Number of Targets: 53 |
| T3D0004 | Vinyl chloride 75-01-4 | C2H3Cl 62.498 g/mol | 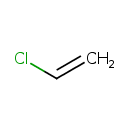 |
| Vinyl chloride poisoning exhibits many of the characteristics of autoimmune diseases. This is believed to be the result of a reactive vinyl chloride intermediate metab...more Number of Targets: 43 |
| T3D0006 | Benzene 71-43-2 | C6H6 78.112 g/mol | 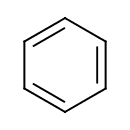 |
| The toxic agents of benzene are its metabolites. Benzene is able increase its toxicity by inducing cytochrome P450 2E1, its main metabolic enzyme. Benzene's primary to...more Number of Targets: 101 |
| T3D0007 | Cadmium 7440-43-9 | Cd 112.410 g/mol | 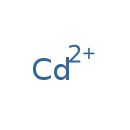 |
| Cadmium initially binds to metallothionein and is transported to the kidney. Toxic effects are observed once the concentration of cadmium exceeds that of available met...more Number of Targets: 27 |
| T3D0009 | Benzo[a]pyrene 50-32-8 | C20H12 252.309 g/mol | 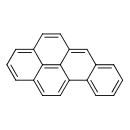 |
| The ability of PAH's to bind to blood proteins such as albumin allows them to be transported throughout the body. Many PAH's induce the expression of cytochrome P450 e...more Number of Targets: 9 |
| T3D0010 | Benzo[b]fluoranthene 205-99-2 | C20H12 252.309 g/mol | 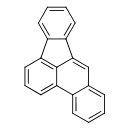 |
| The ability of PAH's to bind to blood proteins such as albumin allows them to be transported throughout the body. Many PAH's induce the expression of cytochrome P450 e...more Number of Targets: 5 |
| T3D0011 | Chloroform 67-66-3 | CHCl3 119.378 g/mol | 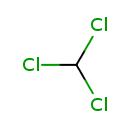 |
| Chloroform and the reactive intermediates of chloroform metabolism, especially phosgene, bind covalently and irreversibly to cellular macromolecules and cause cellular...more Number of Targets: 41 |
| T3D0012 | Clofenotane 50-29-3 | C14H9Cl5 354.486 g/mol | 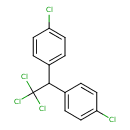 |
| DDT toxicity occurs via at least four mechanisms, possibly all functioning simultaneously. DDT reduces potassium transport across the membrane. DDT inhibits the inacti...more Number of Targets: 64 |
| T3D0013 | Aroclor 1254 11097-69-1 | C12H5Cl5 326.433 g/mol | 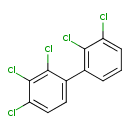 |
| The mechanism of action varies with the specific PCB. Dioxin-like PCBs bind to the aryl hydrocarbon receptor, which disrupts cell function by altering the transcriptio...more Number of Targets: 8 |
| T3D0014 | Aroclor 1260 11096-82-5 | C12H4Cl6 360.878 g/mol | 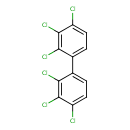 |
| The mechanism of action varies with the specific PCB. Dioxin-like PCBs bind to the aryl hydrocarbon receptor, which disrupts cell function by altering the transcriptio...more Number of Targets: 7 |
| T3D0015 | Dibenzo[a,h]anthracene 53-70-3 | C22H14 278.347 g/mol | 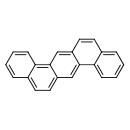 |
| The ability of PAH's to bind to blood proteins such as albumin allows them to be transported throughout the body. Many PAH's induce the expression of cytochrome P450 e...more Number of Targets: 7 |
| T3D0016 | Trichloroethylene 1979-01-06 | C2HCl3 131.388 g/mol | 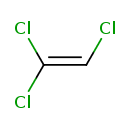 |
| The toxic and carcinogenic effects of trichloroethylene are believed to be caused mainly by its metabolites, including trichloroacetic acid, dichloroacetic acid, and c...more Number of Targets: 50 |
| T3D0017 | Dieldrin 60-57-1 | C12H8Cl6O 380.909 g/mol | 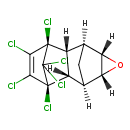 |
| Dieldrin antagonizes the action of the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) acting at the GABA-A receptors, effectively blocking the GABA-induced uptake of ...more Number of Targets: 46 |
| T3D0018 | Hexavalent chromium 18540-29-9 | Cr 51.996 g/mol |  |
| Hexavalent chromium's carcinogenic effects are caused by its metabolites, pentavalent and trivalent chromium. The DNA damage may be caused by hydroxyl radicals produce...more Number of Targets: 5 |
| T3D0019 | White Phosphorus 12185-10-3 | P4 123.895 g/mol |  |
| Exposure to white phosphorus has been shown to damage the rough endoplasmic reticulum and cause a disaggregation of polyribosomes. This damage results in impairment of...more Number of Targets: 0 |
| T3D0020 | Chlordane 57-74-9 | C10H6Cl8 409.779 g/mol |  |
| Chlordane is believed to bind irreversibly to DNA, leading to cell death or altered cellular function. It also affects transcription by antagonizing estrogen-related r...more Number of Targets: 54 |
| T3D0021 | P,P'-DDE 72-55-9 | C14H8Cl4 318.025 g/mol | 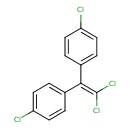 |
| DDE toxicity occurs via at least four mechanisms, possibly all functioning simultaneously. DDE reduces potassium transport across the membrane. DDE inhibits the inacti...more Number of Targets: 60 |
| T3D0022 | Hexachlorobutadiene 87-68-3 | C4Cl6 260.761 g/mol | 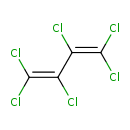 |
| It is believed that intermediates produced by modification of the S- 1,1,2,3,4-pentachlorodienyl cysteine derivative metabolite by gamma-glutamyltransferase are respon...more Number of Targets: 40 |
| T3D0024 | Aldrin 309-00-2 | C12H8Cl6 364.910 g/mol | 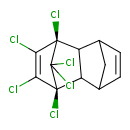 |
| Aldrin antagonizes the action of the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) acting at the GABA-A receptors, effectively blocking the GABA-induced uptake of ch...more Number of Targets: 41 |
| T3D0025 | P,P'-DDD 72-54-8 | C14H10Cl4 320.041 g/mol | 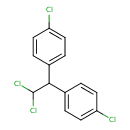 |
| DDD toxicity occurs via at least four mechanisms, possibly all functioning simultaneously. DDD reduces potassium transport across the membrane. DDD inhibits the inacti...more Number of Targets: 62 |
| T3D0026 | Benzidine 92-87-5 | C12H12N2 184.237 g/mol | 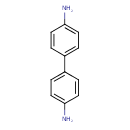 |
| N-acetylated benzidine metabolites are believed to form adducts with nucleic acids. Carcinogenesis is initiated when they are activated by peroxidation by prostaglandi...more Number of Targets: 13 |
| T3D0027 | Aroclor 1248 12672-29-6 | C12H6Cl4 291.988 g/mol | 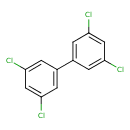 |
| The mechanism of action varies with the specific PCB. Dioxin-like PCBs bind to the aryl hydrocarbon receptor, which disrupts cell function by altering the transcriptio...more Number of Targets: 7 |
| T3D0028 | Cyanide 1957-12-05 | CN 26.018 g/mol |  |
| Organic nitriles decompose into cyanide ions both in vivo and in vitro. Consequently the primary mechanism of toxicity for organic nitriles is their production of toxi...more Number of Targets: 42 |