| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 2.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2009-07-23 18:26:11 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:25:58 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | T3D3090 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Grayanotoxin I |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | Grayanotoxins are toxins found in rhododendrons and other plants of the family Ericaceae. It can be found in honey made from their nectar and cause a very rare poisonous reaction called grayanotoxin poisoning, honey intoxication, or rhododendron poisoning. (1) |
|---|
| Compound Type | - Ester
- Ether
- Natural Compound
- Organic Compound
- Plant Toxin
|
|---|
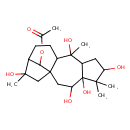
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | | (3beta,6beta,14R)-3,5,6,10,16-Pentahydroxygrayanotoxan-14-yl acetate |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C22H36O7 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 412.517 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 412.246 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 4720-09-6 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | 3,4,6,9,14-pentahydroxy-5,5,9,14-tetramethyltetracyclo[11.2.1.0¹,¹⁰.0⁴,⁸]hexadecan-16-yl acetate |
|---|
| Traditional Name | 3,4,6,9,14-pentahydroxy-5,5,9,14-tetramethyltetracyclo[11.2.1.0¹,¹⁰.0⁴,⁸]hexadecan-16-yl acetate |
|---|
| SMILES | CC(=O)OC1C2CCC3C1(CC2(C)O)CC(O)C1(O)C(CC(O)C1(C)C)C3(C)O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C22H36O7/c1-11(23)29-17-12-6-7-13-20(5,27)14-8-15(24)18(2,3)22(14,28)16(25)9-21(13,17)10-19(12,4)26/h12-17,24-28H,6-10H2,1-5H3 |
|---|
| InChI Key | InChIKey=NXCYBYJXCJWMRY-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as leucothol and grayanotoxane diterpenoids. These are diterpenoids with a structure based either on the leucothol or the grayanotoxane skeleton. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
|---|
| Class | Prenol lipids |
|---|
| Sub Class | Diterpenoids |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Leucothol and grayanotoxane diterpenoids |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Grayanotoxane diterpenoid
- Tertiary alcohol
- Cyclic alcohol
- Secondary alcohol
- Carboxylic acid ester
- Polyol
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organic oxide
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organooxygen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Alcohol
- Aliphatic homopolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic homopolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Exogenous |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | Not Available |
|---|
| Applications | |
|---|
| Biological Roles | |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Appearance | White powder. |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | | Solubility | 28.1 mg/mL at 12°C [SEIDELL,A (1941)] | | LogP | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | View |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-01bd-3309000000-1fa8eb7e1da3343f09df | 2021-09-23 | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-004j-0009100000-5ddf7d9c194fa15b4bbe | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-0fba-0009000000-b9fda3cf49e8fd4e3ed9 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0ufr-0009000000-8da669856576af22490a | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-03dl-1009500000-01c0f615981e0767c5b2 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-0f6x-2009100000-43ce097ad4faf4e8b7df | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0fb9-4509000000-c6f0b485a9a5c03398eb | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-03di-0008900000-e4c9c1a68bd32f0602cb | 2021-10-12 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-000i-0009200000-3ebeb6d15944444a471a | 2021-10-12 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-054o-4928100000-86cb846976a7a9f60f45 | 2021-10-12 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-03di-2000900000-64262917c7823f9be5ee | 2021-10-12 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-0bt9-9006500000-3f3a2de14a2eb410f35a | 2021-10-12 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0a4l-9000100000-9cbe2a357d4800479f4b | 2021-10-12 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-10-13 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-10-13 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-10-13 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-10-13 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-10-13 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-10-13 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-10-13 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-10-13 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-10-13 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-10-13 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-10-13 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-10-13 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-10-13 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-10-13 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-10-13 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-10-13 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-10-13 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-10-13 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-10-13 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-10-13 | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Oral (ingestion) (2) ; dermal (2) |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Grayanotoxins bind to specific sodium ion channels in cell membranes. The grayanotoxins prevent inactivation, leaving excitable cells depolarized. (1) |
|---|
| Metabolism | Not Available |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | Not Available |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | Grayanotoxins are toxins found in rhododendrons and other plants of the family Ericaceae. (1) |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | Grayanotoxins affect the nervous system but are not usually fatal. (1) |
|---|
| Symptoms | Initial symptoms include excessive salivation, perspiration, vomiting, dizziness, weakness and paresthesia in the extremities and around the mouth, low blood pressure and sinus bradycardia. In higher doses symptoms can include loss of coordination, severe and progressive muscular weakness, bradycardia (and, paradoxically, ventricular tachycardia), and nodal rhythm or Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. (1) |
|---|
| Treatment | Medical treatment is not often needed but sometimes atropine therapy, vasopressors and other agents are used to mitigate symptoms. (1) |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | Not Available |
|---|
| HMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 19604097 |
|---|
| ChEMBL ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChemSpider ID | Not Available |
|---|
| KEGG ID | Not Available |
|---|
| UniProt ID | Not Available |
|---|
| OMIM ID | |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| CTD ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Stitch ID | Grayanotoxin I |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ACToR ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| MSDS | Not Available |
|---|
| General References | - Wikipedia. Grayanotoxin. Last Updated 13 September 2009. [Link]
- Wikipedia. Phytotoxin. Last Updated 7 August 2009. [Link]
|
|---|
| Gene Regulation |
|---|
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|