
Browsing Toxins
Displaying toxin 676 - 700 of 3678 in total
| T3DB ID | Name CAS Number | Formula Weight | Structure | Type | Mechanism of Toxicity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T3D0794 | Actinolite Asbestos 77536-66-4 | (Na, K)0-1Ca2(Mg, Fe)5Si8O22(OH)2 Not Available |  |
| When asbestos fibers are inhaled, many are deposited on the epithelial surface of the respiratory tree. Fibers that are retained in the lung or mesothelium for long pe...more Number of Targets: 1 |
| T3D0795 | Anthophyllite Asbestos 77536-67-5 | (Na, K)0-1Mg2(Mg, Fe)5Si8O22(OH)2, Mg/(Mg + Fe) > 0.6 Not Available |  |
| When asbestos fibers are inhaled, many are deposited on the epithelial surface of the respiratory tree. Fibers that are retained in the lung or mesothelium for long pe...more Number of Targets: 1 |
| T3D0796 | Tin 7440-31-5 | Sn 118.710 g/mol |  |
| Organotin compounds produce neurotoxic and immunotoxic effects. Organotins may directly activate glial cells contributing to neuronal cell degeneration by local releas...more Number of Targets: 15 |
| T3D0797 | Imidacloprid 105827-78-9 | C9H10ClN5O2 255.661 g/mol |  |
| Imidacloprid acts on the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor; the chlorination inhibits degradation by acetylcholine-esterase (L1130). Number of Targets: 12 |
| T3D0798 | Fipronil 120068-37-3 | C12H4Cl2F6N4OS 437.148 g/mol |  |
| Fipronil blocks the passage of chloride ions through the GABA-regulated chloride channel, disrupting CNS activity. (T10) Organic nitriles decompose into cyanide ions b...more Number of Targets: 29 |
| T3D0799 | Nicotine 54-11-5 | C10H14N2 162.232 g/mol |  |
| Nicotine is a stimulant drug that acts as an agonist at nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. These are ionotropic receptors composed up of five homomeric or heteromeric ...more Number of Targets: 22 |
| T3D0800 | Rotenone 83-79-4 | C20H18O6 354.353 g/mol |  |
| Rotenone works by interfering with the electron transport chain in mitochondria. Specifically, it inhibits the transfer of electrons from iron-sulfur centers in comple...more Number of Targets: 47 |
| T3D0801 | Dichlorprop 120-36-5 | C9H8Cl2O3 235.064 g/mol |  |
| CDDs cause their toxic effects by binding to the aryl hydrocarbon receptor and subsequently altering the trascription of certain genes. The affinity for the Ah recepto...more Number of Targets: 6 |
| T3D0802 | 2,4-Dichlorophenoxybutyric acid 94-82-6 | C10H10Cl2O3 249.091 g/mol |  |
| Some of the endocrine effects of 2,4-DB may be mediated by the 2,4-D mediated displacement of sex hormones from the sex hormone binding globulin or the 2,4-D mediated ...more Number of Targets: 9 |
| T3D0803 | 2,4,5-Trichlorophenoxyacetic acid 93-76-5 | C8H5Cl3O3 255.483 g/mol |  |
| CDDs cause their toxic effects by binding to the aryl hydrocarbon receptor and subsequently altering the trascription of certain genes. The affinity for the Ah recepto...more Number of Targets: 3 |
| T3D0804 | 2-Methyl-4-chlorophenoxyacetic acid 94-74-6 | C9H9ClO3 200.619 g/mol |  |
| CDDs cause their toxic effects by binding to the aryl hydrocarbon receptor and subsequently altering the trascription of certain genes. The affinity for the Ah recepto...more Number of Targets: 6 |
| T3D0805 | 4-(4-Chloro-2-methylphenoxy)butanoic acid 94-81-5 | C11H13ClO3 228.672 g/mol |  |
| Not Available Number of Targets: 3 |
| T3D0806 | Methylchlorophenoxypropionic acid 93-65-2 | C10H11ClO3 214.646 g/mol | 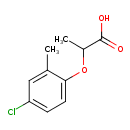 |
| CDDs cause their toxic effects by binding to the aryl hydrocarbon receptor and subsequently altering the trascription of certain genes. The affinity for the Ah recepto...more Number of Targets: 3 |
| T3D0807 | Dicamba 1918-00-9 | C8H6Cl2O3 221.037 g/mol |  |
| Not Available Number of Targets: 5 |
| T3D0808 | Paraquat dichloride 1910-42-5 | C12H14Cl2N2 257.159 g/mol | 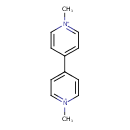 |
| The mechanisms of the toxic effects of paraquat are largely the result of a metabolically catalyzed single electron oxidation reduction reaction, resulting in depletio...more Number of Targets: 4 |
| T3D0810 | Alachlor 15972-60-8 | C14H20ClNO2 269.767 g/mol |  |
| Its mode of action is elongase inhibition, and inhibition of geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (GGPP) cyclisation enzymes. It is also know to inhibit biosynthesis of fatty...more Number of Targets: 26 |
| T3D0811 | Acetochlor 34256-82-1 | C14H20ClNO2 269.767 g/mol |  |
| Its mode of action is elongase inhibition, and inhibition of geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (GGPP) cyclisation enzymes (L920). Number of Targets: 23 |
| T3D0812 | Glufosinate 51276-47-2 | C5H12NO4P 181.127 g/mol |  |
| Glufosinate irreversibly inhibits the enzyme glutamine synthetase, which decreases ammonia detoxification. Increased ammonia levels lead to impairment of photorespirat...more Number of Targets: 1 |
| T3D0813 | Amygdalin 29883-15-6 | C20H27NO11 457.429 g/mol |  |
| Amygdalin can be metabolized into hydrogen cyanide in the stomach causing discomfort or illness. (L402) Organic nitriles decompose into cyanide ions both in vivo and i...more Number of Targets: 0 |
| T3D0815 | Angelicin 523-50-2 | C11H6O3 186.164 g/mol |  |
| The mechanism of action many furocoumarins is based on their ability to form photoadducts with DNA and other cellular components such as RNA, proteins, and several pro...more Number of Targets: 4 |
| T3D0816 | Isobergapten 482-48-4 | C12H8O4 216.190 g/mol |  |
| Inhibits insect cytochrome P450 (L579). The mechanism of action many furocoumarins is based on their ability to form photoadducts with DNA and other cellular component...more Number of Targets: 3 |
| T3D0819 | Sphondin 483-66-9 | C12H8O4 216.190 g/mol |  |
| Sphondin possesses an inhibitory effect on IL-1b-induced COX-2 protein expression and PGE2 release in human pulmonary epithelial cell line (A549). The mechanism of act...more Number of Targets: 3 |
| T3D0821 | Heratomin 61265-06-3 | C16H14O4 270.280 g/mol | 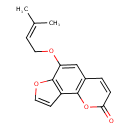 |
| The mechanism of action many furocoumarins is based on their ability to form photoadducts with DNA and other cellular components such as RNA, proteins, and several pro...more Number of Targets: 3 |
| T3D0822 | Pimpinellin 131-12-4 | C13H10O5 246.216 g/mol |  |
| Pimpinellin acts as antagonist of proteins with GABA receptor activity (L579). The mechanism of action many furocoumarins is based on their ability to form photoadduct...more Number of Targets: 3 |
| T3D0825 | Psoralen 66-97-7 | C11H6O3 186.164 g/mol |  |
| The mechanism of action many furocoumarins is based on their ability to form photoadducts with DNA and other cellular components such as RNA, proteins, and several pro...more Number of Targets: 4 |