| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 2.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2009-07-23 18:26:18 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:25:59 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | T3D3103 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Fumarin |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | Fumarin is an anticoagulant and rodenticide derived from coumarin. (3) |
|---|
| Compound Type | - Aromatic Hydrocarbon
- Ester
- Organic Compound
- Pesticide
- Synthetic Compound
|
|---|
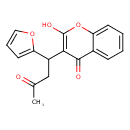
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | | 3-(1-Furyl-3-acetylethyl)-4-hydroxycoumarin | | 3-(a-Furyl-b-acetylaethyl)-4-hydroxycumarin | | 3-(alpha-Acetonyl-2-furylmethyl)-4-hydroxycoumarin | | 3-(alpha-Acetonylfurfuryl)-4-hydroxycoumarin | | 3-(alpha-Acetonylfuryl)-4-hydroxy-coumarin | | 3-(alpha-Furyl-beta-acetylaethyl)-4-hydroxycumarin | | 3-[1-(2-Furyl)-3-oxobutyl]-4-hydroxy-2H-chromen-2-one | | 4-(2-Furyl)-4-(4-hydroxy-3-coumarinyl)-2-butanone | | 4-(2-Furyl)-4-(4-hydroxy-3-kumarinyl)-2-butanon | | Coumafuryl | | Cumafuryl | | Foumarin | | Fumasol | | Furmarin | | Kill-ko rat | | Krumkil | | Kumatox | | Lurat | | Mouse blues | | Rat-a-way | | Ratafin | | Tomarin |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C17H14O5 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 298.290 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 298.084 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 117-52-2 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | 3-[1-(furan-2-yl)-3-oxobutyl]-2-hydroxy-4H-chromen-4-one |
|---|
| Traditional Name | fumarin |
|---|
| SMILES | CC(=O)CC(C1=CC=CO1)C1=C(O)OC2=CC=CC=C2C1=O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C17H14O5/c1-10(18)9-12(13-7-4-8-21-13)15-16(19)11-5-2-3-6-14(11)22-17(15)20/h2-8,12,20H,9H2,1H3 |
|---|
| InChI Key | InChIKey=VGVYRHYDNGFIGF-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as coumarins and derivatives. These are polycyclic aromatic compounds containing a 1-benzopyran moiety with a ketone group at the C2 carbon atom (1-benzopyran-2-one). |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Phenylpropanoids and polyketides |
|---|
| Class | Coumarins and derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Not Available |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Coumarins and derivatives |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Chromone
- Coumarin
- Benzopyran
- 1-benzopyran
- Pyranone
- Pyran
- Benzenoid
- Heteroaromatic compound
- Furan
- Vinylogous acid
- Ketone
- Oxacycle
- Organoheterocyclic compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organooxygen compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organic oxide
- Carbonyl group
- Aromatic heteropolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Exogenous |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | Not Available |
|---|
| Applications | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Appearance | White powder. |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | 124°C | | Boiling Point | Not Available | | Solubility | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | View |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-000t-0090000000-0cd7f2dee8d2f3eca0b6 | 2016-06-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-001j-1290000000-3885f4b00eeecf0dc457 | 2016-06-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-03di-4490000000-51e23f1dc99fe4fe53e4 | 2016-06-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-0f6t-0090000000-b119a3e79640f86bd3cf | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-0nmj-2590000000-9606cfac8f7e64951349 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-052o-9650000000-f28b41cceeb557808759 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Oral (ingestion) (5) ; dermal (5) |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Fumarin inhibits the enzyme Vitamin K epoxide reductase. This enzyme is needed for the reconstitution of the vitamin K in its cycle from vitamin K-epoxide, and so fumarin steadily decreases the level of active vitamin K in the blood. Vitamin K is required for the synthesis of important substances including prothrombin, which is involved in blood clotting. This disruption becomes increasingly severe until the blood effectively loses any ability to clot. In addition, fumarin increases permeability of blood capillaries. The blood plasma and blood itself begins to leak from the blood vessels, causing internal bleeding leading to shock, loss of consciousness, and eventually death. (4) |
|---|
| Metabolism | Not Available |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | LD50: 14.7 mg/kg (Oral, Mouse) (1) |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | Fumarin is a rodenticide. (3) |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | Fumarin is an anticoagulant and causes internal bleeding, leading to shock, loss of consciousness, and eventually death. (4) |
|---|
| Symptoms | Fumarin initially causes dehydration before progressing to bleeding complications. (4) |
|---|
| Treatment | The primary antidote to fumarin poisoning is immediate administration of vitamin K1 (initially slow intravenous injections of 10-25 mg repeated all 3-6 hours until normalisation of the prothrombin time; then 10 mg orally four times daily as a "maintenance dose"). It is an extremely effective antidote, provided the poisoning is caught before too much damage has been done to the victim's circulatory system. At high doses fumarin can affect the body for many months, and the antidote must be administered regularly for a long period of time. (4) |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | Not Available |
|---|
| HMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 8335 |
|---|
| ChEMBL ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChemSpider ID | 8032 |
|---|
| KEGG ID | Not Available |
|---|
| UniProt ID | Not Available |
|---|
| OMIM ID | |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| CTD ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Stitch ID | Fumarin |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ACToR ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| MSDS | T3D3103.pdf |
|---|
| General References | - Meijerman I, Beijnen JH, Schellens JH: Herb-drug interactions in oncology: focus on mechanisms of induction. Oncologist. 2006 Jul-Aug;11(7):742-52. [16880233 ]
- Farm Chemicals Handbook (2002).Willoughby, OH: Meister Publishing.
- Wikipedia. Coumarin. Last Updated 21 July 2009. [Link]
- Wikipedia. Brodifacoum. Last Updated 22 June 2009. [Link]
- Wikipedia. Phytotoxin. Last Updated 7 August 2009. [Link]
|
|---|
| Gene Regulation |
|---|
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|