
Browsing Toxins
Displaying toxin 1101 - 1125 of 3678 in total
| T3DB ID | Name CAS Number | Formula Weight | Structure | Type | Mechanism of Toxicity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T3D1323 | Lead oxalate 814-93-7 | C2O4Pb 295.200 g/mol |  |
| Lead mimics other biologically important metals, such as zinc, calcium, and iron, competing as cofactors for many of their respective enzymatic reactions. For example,...more Number of Targets: 29 |
| T3D1324 | Lead stearate 1072-35-1 | C36H70O4Pb 774.100 g/mol |  |
| Lead mimics other biologically important metals, such as zinc, calcium, and iron, competing as cofactors for many of their respective enzymatic reactions. For example,...more Number of Targets: 29 |
| T3D1325 | Lead selenide 12069-00-0 | PbSe 286.200 g/mol |  |
| Lead mimics other biologically important metals, such as zinc, calcium, and iron, competing as cofactors for many of their respective enzymatic reactions. For example,...more Number of Targets: 29 |
| T3D1326 | Lead telluride 1314-91-6 | PbTe 334.800 g/mol |  |
| Lead mimics other biologically important metals, such as zinc, calcium, and iron, competing as cofactors for many of their respective enzymatic reactions. For example,...more Number of Targets: 29 |
| T3D1327 | Lead fluoride 7783-46-2 | F2Pb 245.200 g/mol |  |
| Lead mimics other biologically important metals, such as zinc, calcium, and iron, competing as cofactors for many of their respective enzymatic reactions. For example,...more Number of Targets: 29 |
| T3D1328 | Lead hydroxide 19781-14-3 | H2O2Pb 241.200 g/mol |  |
| Lead mimics other biologically important metals, such as zinc, calcium, and iron, competing as cofactors for many of their respective enzymatic reactions. For example,...more Number of Targets: 29 |
| T3D1329 | Plumbane 15875-18-0 | H4Pb 211.200 g/mol |  |
| Lead mimics other biologically important metals, such as zinc, calcium, and iron, competing as cofactors for many of their respective enzymatic reactions. For example,...more Number of Targets: 29 |
| T3D1330 | Basic lead carbonate 1319-46-6 | C2H2O8Pb3 775.600 g/mol |  |
| Lead mimics other biologically important metals, such as zinc, calcium, and iron, competing as cofactors for many of their respective enzymatic reactions. For example,...more Number of Targets: 29 |
| T3D1331 | Lead subacetate 1335-32-6 | C4H10O8Pb3 807.700 g/mol |  |
| Lead mimics other biologically important metals, such as zinc, calcium, and iron, competing as cofactors for many of their respective enzymatic reactions. For example,...more Number of Targets: 29 |
| T3D1332 | Lead tetraacetate 546-67-8 | C8H12O8Pb 443.400 g/mol |  |
| Lead mimics other biologically important metals, such as zinc, calcium, and iron, competing as cofactors for many of their respective enzymatic reactions. For example,...more Number of Targets: 29 |
| T3D1333 | Lead tungstate 7759-01-5 | O4PbW 455.000 g/mol |  |
| Lead mimics other biologically important metals, such as zinc, calcium, and iron, competing as cofactors for many of their respective enzymatic reactions. For example,...more Number of Targets: 29 |
| T3D1334 | Lead thiosulfate 26265-65-6 | O3PbS2 319.300 g/mol | 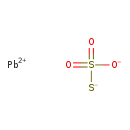 |
| Lead mimics other biologically important metals, such as zinc, calcium, and iron, competing as cofactors for many of their respective enzymatic reactions. For example,...more Number of Targets: 29 |
| T3D1335 | Lead perchlorate 13637-76-8 | Cl2O8Pb 406.100 g/mol | 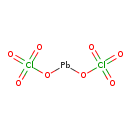 |
| Lead mimics other biologically important metals, such as zinc, calcium, and iron, competing as cofactors for many of their respective enzymatic reactions. For example,...more Number of Targets: 29 |
| T3D1337 | Basic lead acetate 51404-69-4 | C2H4O3Pb 283.300 g/mol | 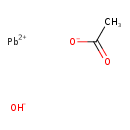 |
| Lead mimics other biologically important metals, such as zinc, calcium, and iron, competing as cofactors for many of their respective enzymatic reactions. For example,...more Number of Targets: 29 |
| T3D1338 | Diethyldimethyl lead 1762-27-2 | C6H16Pb 295.400 g/mol | 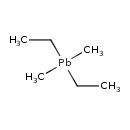 |
| Lead mimics other biologically important metals, such as zinc, calcium, and iron, competing as cofactors for many of their respective enzymatic reactions. For example,...more Number of Targets: 29 |
| T3D1339 | Methyltriethyl lead 1762-28-3 | C7H18Pb 309.400 g/mol | 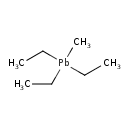 |
| Lead mimics other biologically important metals, such as zinc, calcium, and iron, competing as cofactors for many of their respective enzymatic reactions. For example,...more Number of Targets: 29 |
| T3D1340 | Ethyltrimethyl lead 1762-26-1 | C5H14Pb 281.400 g/mol | 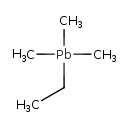 |
| Lead mimics other biologically important metals, such as zinc, calcium, and iron, competing as cofactors for many of their respective enzymatic reactions. For example,...more Number of Targets: 29 |
| T3D1341 | Mercuric amidochloride 10124-48-8 | ClH2HgN 252.070 g/mol |  |
| High-affinity binding of the divalent mercuric ion to thiol or sulfhydryl groups of proteins is believed to be the major mechanism for the activity of mercury. Through...more Number of Targets: 50 |
| T3D1342 | Mercury(I) fluoride 13967-25-4 | F2Hg2 439.180 g/mol |  |
| High-affinity binding of the divalent mercuric ion to thiol or sulfhydryl groups of proteins is believed to be the major mechanism for the activity of mercury. Through...more Number of Targets: 50 |
| T3D1343 | Mercury(II) fluoride 7783-39-3 | F2Hg 238.590 g/mol |  |
| High-affinity binding of the divalent mercuric ion to thiol or sulfhydryl groups of proteins is believed to be the major mechanism for the activity of mercury. Through...more Number of Targets: 50 |
| T3D1344 | Mercury(I) oxide 15829-53-5 | Hg2O 417.180 g/mol |  |
| High-affinity binding of the divalent mercuric ion to thiol or sulfhydryl groups of proteins is believed to be the major mechanism for the activity of mercury. Through...more Number of Targets: 50 |
| T3D1345 | Mercury oxide sulfate 1312-03-4 | Hg3O6S 729.830 g/mol |  |
| High-affinity binding of the divalent mercuric ion to thiol or sulfhydryl groups of proteins is believed to be the major mechanism for the activity of mercury. Through...more Number of Targets: 50 |
| T3D1346 | Cadmium mercury sulfide 1345-09-1 | CdHgS2 377.130 g/mol |  |
| Cadmium initially binds to metallothionein and is transported to the kidney. Toxic effects are observed once the concentration of cadmium exceeds that of available met...more Number of Targets: 69 |
| T3D1347 | Mercuric potassium cyanide 591-89-9 | C4HgK2N4 382.860 g/mol |  |
| High-affinity binding of the divalent mercuric ion to thiol or sulfhydryl groups of proteins is believed to be the major mechanism for the activity of mercury. Through...more Number of Targets: 91 |
| T3D1348 | Mercuric benzoate 583-15-3 | C14H10HgO4 442.820 g/mol |  |
| High-affinity binding of the divalent mercuric ion to thiol or sulfhydryl groups of proteins is believed to be the major mechanism for the activity of mercury. Through...more Number of Targets: 50 |