| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 2.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2009-11-23 23:08:08 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:26:14 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | T3D3626 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Diazolidinyl urea |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | Diazolidinyl urea is an antimicrobial preservative that acts as a formaldehyde releaser. It is used in many cosmetics, skin care products, shampoos and conditioners, as well as a wide range of products including bubble baths, baby wipes and household detergents. Diazolidinyl urea is found in the commercially available preservative Germaben. Diazolidinyl urea may cause contact dermatitis. Its toxicity is also due to it's ability to release formaldehyde, which is believed to be carcinogenic. (3) |
|---|
| Compound Type | - Amide
- Amine
- Cosmetic Toxin
- Household Toxin
- Organic Compound
- Synthetic Compound
|
|---|
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | | Diazolidinylurea | | Germall 11 | | Germall II | | Imidazolidinyl urea 11 | | N-(1,3-Bis(hydroxymethyl)-2,5-dioxo-4-imidazolidinyl)-N,n'-bis(hydroxymethyl) urea |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C8H14N4O7 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 278.219 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 278.086 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 78491-02-8 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | 1-[1,3-bis(hydroxymethyl)-2,5-dioxoimidazolidin-4-yl]-1,3-bis(hydroxymethyl)urea |
|---|
| Traditional Name | diazolidinyl urea |
|---|
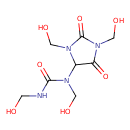
| SMILES | OCNC(=O)N(CO)C1N(CO)C(=O)N(CO)C1=O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C8H14N4O7/c13-1-9-7(18)10(2-14)5-6(17)12(4-16)8(19)11(5)3-15/h5,13-16H,1-4H2,(H,9,18) |
|---|
| InChI Key | InChIKey=SOROIESOUPGGFO-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as allantoins. These are heterocyclic compounds containing an imiazolidine ring substituted by a ketone group at positions 2 and 5, and an urea at position 4. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organoheterocyclic compounds |
|---|
| Class | Azolidines |
|---|
| Sub Class | Imidazolidines |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Allantoins |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Allantoin
- Alpha-amino acid or derivatives
- Ureide
- N-acyl urea
- Dicarboximide
- Urea
- Carbonic acid derivative
- Alkanolamine
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Azacycle
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Organooxygen compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organic oxide
- Carbonyl group
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Aliphatic heteromonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic heteromonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Exogenous |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | Not Available |
|---|
| Applications | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Appearance | White powder. |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | | Solubility | 1000 mg/mL at 25°C | | LogP | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | View |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-014i-0390000000-145fdee36d825d8eb8f0 | 2016-08-01 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-00xr-0970000000-c286f9a082ee211e393e | 2016-08-01 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-00di-0930000000-fe1c7215f52092ff48e7 | 2016-08-01 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-016s-0190000000-2ae8acf690107ac94f31 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-014j-2090000000-c8ec0d76384135b50089 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-006w-4920000000-3b81c399001b1e89090b | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Oral (2) ; inhalation (2) ; dermal (2) |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Diazolidinyl urea is a formaldehyde releaser. It is likely that formaldehyde toxicity occurs when intracellular levels saturate formaldehyde dehydrogenase activity, allowing the unmetabolized intact molecule to exert its effects. Formaldehyde is known to form cross links between protein and DNA and undergo metabolic incorporation into macromolecules (DNA, RNA, and proteins). (2, 3) |
|---|
| Metabolism | Formaldehyde may be absorbed following inhalation, oral, or dermal exposure. It is an essential metabolic intermediate in all cells and is produced during the normal metabolism of serine, glycine, methionine, and choline and also by the demethylation of N-, S-, and O-methyl compounds. Exogenous formaldehyde is metabolized to formate by the enzyme formaldehyde dehydrogenase at the initial site of contact. After oxidation of formaldehyde to formate, the carbon atom is further oxidized to carbon dioxide or incorporated into purines, thymidine, and amino acids via tetrahydrofolatedependent one-carbon biosynthetic pathways. Formaldehyde is not stored in the body and is excreted in the urine (primarily as formic acid), incorporated into other cellular molecules, or exhaled as carbon dioxide. (2) |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | Not Available |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | 1, carcinogenic to humans (for formaldehyde). (1) |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | Diazolidinyl urea is an antimicrobial preservative used in many cosmetics, skin care products, shampoos and conditioners, as well as a wide range of products including bubble baths, baby wipes and household detergents. Diazolidinyl urea is found in the commercially available preservative Germaben. (3) |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | Diazolidinyl urea releases formaldehyde, a known human carcinogen. (2, 3) |
|---|
| Symptoms | Some people have a contact allergy to diazolidinyl urea, causing dermatitis. (3) |
|---|
| Treatment | Not Available |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | Not Available |
|---|
| HMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 62277 |
|---|
| ChEMBL ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChemSpider ID | 56078 |
|---|
| KEGG ID | Not Available |
|---|
| UniProt ID | Not Available |
|---|
| OMIM ID | |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| CTD ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Stitch ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ACToR ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Diazolidinyl_urea |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| MSDS | T3D3626.pdf |
|---|
| General References | - International Agency for Research on Cancer (2014). IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. [Link]
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (1999). Toxicological profile for formaldehyde. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- Wikipedia. Diazolidinyl urea. Last Updated 29 October 2009. [Link]
|
|---|
| Gene Regulation |
|---|
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|