| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 2.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2009-07-30 17:59:01 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:26:07 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | T3D3521 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Metaldehyde |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | Metaldehyde is a cyclic tetramer of acetaldehyde commonly used as a pesticide against slugs, snails, and other gastropods. Metaldehyde intoxication leads to central nervous system depression, and liver and kidney injury. (1) |
|---|
| Compound Type | - Household Toxin
- Lachrymator
- Organic Compound
- Pesticide
- Synthetic Compound
|
|---|
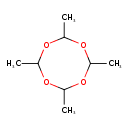
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | | 2,4,6,8-Tetramethyl-1,3,5,7-tetraoxacyclooctane | | 2,4,6,8-Tetramethyl-1,3,5,7-tetroxocane | | Acetaldehyde tetramer | | Agrimort | | Ariotox | | Cekumeta | | Corry's slug death | | Halizan | | Helarion | | Lumacrusk5 | | Metacetaldehyde | | Metaldehyd | | Metaldeide | | Puzomor | | r-2,c-4,c-6,c-8-Tetramethyl-1,3,5,7-tetroxocane | | Slug-tox | | Snail-kil | | Suprasnail |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C8H16O4 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 176.210 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 176.105 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 108-62-3 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | 2,4,6,8-tetramethyl-1,3,5,7-tetraoxocane |
|---|
| Traditional Name | metaldehyde |
|---|
| SMILES | CC1OC(C)OC(C)OC(C)O1 |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C8H16O4/c1-5-9-6(2)11-8(4)12-7(3)10-5/h5-8H,1-4H3 |
|---|
| InChI Key | InChIKey=GKKDCARASOJPNG-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as acetals. Acetals are compounds having the structure R2C(OR')2 ( R' not Hydrogen) and thus diethers of geminal diols. Originally, the term was confined to derivatives of aldehydes (one R = H), but it now applies equally to derivatives of ketones (neither R = H ). Mixed acetals have different R' groups. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic oxygen compounds |
|---|
| Class | Organooxygen compounds |
|---|
| Sub Class | Ethers |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Acetals |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Oxacycle
- Organoheterocyclic compound
- Acetal
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Aliphatic heteromonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic heteromonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Exogenous |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | Not Available |
|---|
| Applications | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Appearance | Colourless or white powder crystals with a mild characteristic odour. (2) |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | 246°C | | Boiling Point | 110-120 °C | | Solubility | 200 mg/L (at 17 °C) | | LogP | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | View |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0043-9600000000-aff896a31bab36179c25 | 2021-09-24 | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-004i-1900000000-3a0583ef3e71ce6c831d | 2016-08-01 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-000j-9200000000-bc04a03537d8c1fc6e1b | 2016-08-01 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-004i-9000000000-fb4cb731680420af219e | 2016-08-01 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-004i-0900000000-1fbd74de738f9bd884cc | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-004i-2900000000-1526b460542bcfef4922 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0a4l-9100000000-9c9a1554992bbbe5388a | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-004i-0900000000-ca808b2786d3287a7be2 | 2021-10-12 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-004i-2900000000-5a5f4674bce9964d8be1 | 2021-10-12 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-006t-9100000000-c5f5078331472e7678c9 | 2021-10-12 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-05i9-9500000000-7198ed360e8398923d71 | 2021-10-12 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-052f-9000000000-e7d24bbcda04dd8a7b2f | 2021-10-12 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-052f-9100000000-7de1757678e99237833f | 2021-10-12 | View Spectrum | | MS | Mass Spectrum (Electron Ionization) | splash10-0002-9000000000-addd53e7c97dd0a41373 | 2014-09-20 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-10-25 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-10-25 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-10-25 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-10-25 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-10-25 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-10-25 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-10-25 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-10-25 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-10-25 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-10-25 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-10-25 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-10-25 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-10-25 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-10-25 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-10-25 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-10-25 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-10-25 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-10-25 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-10-25 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-10-25 | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Oral (1) ; inhalation (1) ; dermal (1) |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | The toxicologically active substance in metaldehyde intoxication is mainly the degradation product acetaldehyde; other toxic products are probably also formed. Acetaldehyde acts as a releasing factor for 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) and noradrenaline (NA). It also competitively inhibits biogenic amine oxidation which, in turn, decreases 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA), a metabolite of 5-HT by competitively inhibiting 5-HT-oxidation. Acetaldehyde also increases monoamine oxidase activity and decreases central serotonin levels. (1) |
|---|
| Metabolism | Metaldehyde is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and may be absorbed from the skin or lungs. Metaldehyde slowly hydrolyses to acetaldehyde in acid solutions (i.e., in the stomach). Acetaldehyde is then oxidized to acetic acid. (2) |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | LD50: 630 mg/kg (Oral, Rat) (1)
LD50: 600 mg/kg (Oral, Dog) (1) |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | 50 to 500 mg/kg orally for an adult human. (1) |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | Metaldehyde is used as a pesticide against slugs, snails, and other gastropods, it is also used in tablets as a solid fuel for small heaters, and as fire-starter. (1)
|
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | Metaldehyde intoxicatin leads to central nervous system depression, and liver and kidney injury. Death from respiratory failure can occur within a few hours of exposure. (2)
|
|---|
| Symptoms | Ingestion is the most common route of metaldehyde poisoning. One to three hours after ingestion the following can occur: severe abdominal pain, nausea, salivation, vomiting, facial flushing, gastroenteritis, diarrhoea, metabolic acidosis, a marked rise in body temperature, drowsiness, convulsions, muscular rigidity, spasms, rhabdomyolysis and coma. Pulse and respiratory rate become progressively slower. Liver and kidney injury occurs at a later stage. Metaldehyde fumes may cause somnolence, uncoordinated movements, nausea, dizziness, CNS-depression, convulsions, and coma. Metaldehyde is also irritant to eyes and skin. (2) |
|---|
| Treatment | Measures to eliminate the substance from the gastrointestinal tract should be especially emphasized because metaldehyde is slowly absorbed and eliminated in the gastrointestinal tract. There is no specific antidote. (2) |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | Not Available |
|---|
| HMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 61021 |
|---|
| ChEMBL ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChemSpider ID | Not Available |
|---|
| KEGG ID | C00084 |
|---|
| UniProt ID | Not Available |
|---|
| OMIM ID | 100650 |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 15343 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | ACETALD |
|---|
| CTD ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Stitch ID | Metaldehyde |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ACToR ID | 7888 |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Metaldehyde |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| MSDS | T3D3521.pdf |
|---|
| General References | - Wikipedia. Metaldehyde. Last updated 22 July 2009. [Link]
- International Programme on Chemical Safety (IPCS) INCHEM (1995). Poison Information Monograph for Metaldehyde. [Link]
|
|---|
| Gene Regulation |
|---|
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|