| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 2.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2009-06-17 23:53:05 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:23:01 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | T3D0996 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Potassium asulam |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | Potassium asulam is a thiocarbamate herbicide invented by May & Baker Ltd, part of the Rhône-Poulenc Group. It is used to kill bracken and docks. Thiocarbamates are mainly used in agriculture as insecticides, herbicides, and fungicides. Additional uses are as biocides for industrial or other commercial applications, and in household products. Some are used for vector control in public health. Thiocarbamates are mostly liquids or solids with low melting points. |
|---|
| Compound Type | - Amide
- Amine
- Carbamate
- Ether
- Herbicide
- Organic Compound
- Synthetic Compound
|
|---|
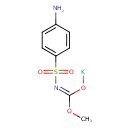
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | | Asulam potassium salt | | Asulam-potassium | | Carbamic acid, sulfanilyl-, methyl ester, potassium salt | | Potassium, (N1-carboxysulfanilamido)-, methyl ester | | Potassium, (N1-carboxysulfanilamido)-, methyl ester (7CI) |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C8H9KN2O4S |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 268.331 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 267.992 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 14089-43-1 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | 4-{[(Z)-[methoxy(potassiooxy)methylidene]amino]sulfonyl}aniline |
|---|
| Traditional Name | 4-[(Z)-[methoxy(potassiooxy)methylidene]aminosulfonyl]aniline |
|---|
| SMILES | CO\C(O[K])=N\S(=O)(=O)C1=CC=C(N)C=C1 |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C8H10N2O4S.K/c1-14-8(11)10-15(12,13)7-4-2-6(9)3-5-7;/h2-5H,9H2,1H3,(H,10,11);/q;+1/p-1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | InChIKey=WKJOGZIRDGAEFO-UHFFFAOYSA-M |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as benzenesulfonamides. These are organic compounds containing a sulfonamide group that is S-linked to a benzene ring. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Benzenoids |
|---|
| Class | Benzene and substituted derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Benzenesulfonamides |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Benzenesulfonamides |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Benzenesulfonamide
- Benzenesulfonyl group
- Aniline or substituted anilines
- Sulfonyl
- Organosulfonic acid or derivatives
- Organic sulfonic acid or derivatives
- Organic alkali metal salt
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organic oxide
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organic potassium salt
- Organic salt
- Organic zwitterion
- Primary amine
- Organosulfur compound
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Amine
- Aromatic homomonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic homomonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Exogenous |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | Not Available |
|---|
| Applications | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Appearance | White powder |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | | Solubility | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | View |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-014i-0090000000-bd7e469b10b49c3899d6 | 2019-02-22 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-00di-1920000000-5568a530d0cd354c4c73 | 2019-02-22 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0059-9000000000-b4382b25f237e8703a88 | 2019-02-22 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-014i-1190000000-61f46c19b2cc2275bb59 | 2019-02-23 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-0aor-1890000000-f6c36dee1611bf4150ea | 2019-02-23 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-052p-9630000000-815ce195ebce8f350dcc | 2019-02-23 | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Inhalation (1) ; oral (1); dermal (1) |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Some thiocarbamates (EPTC, Molinate, Pebulate, and Cycloate) share a common mechanism of toxicity, i.e. the inhibition of acetylcholinesterase. An acetylcholinesterase inhibitor suppresses the action of acetylcholine esterase. Because of its essential function, chemicals that interfere with the action of acetylcholine esterase are potent neurotoxins, causing excessive salivation and eye-watering in low doses. Headache, salivation, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain and diarrhea are often prominent at higher levels of exposure. Acetylcholine esterase breaks down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, which is released at nerve and muscle junctions, in order to allow the muscle or organ to relax. The result of acetylcholine esterase inhibition is that acetylcholine builds up and continues to act so that any nerve impulses are continually transmitted and muscle contractions do not stop. |
|---|
| Metabolism | As a general rule, thiocarbamates can be absorbed via the skin, mucous membranes, and the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts. They are eliminated quite rapidly, mainly via expired air and urine. Two major pathways exist for the metabolism of thiocarbamates in mammals. One is via sulfoxidation and conjugation with glutathione. The conjugation product is then cleaved to a cysteine derivative, which is metabolized to a mercapturic acid compound. The second route is oxidation of the sulfur to a sulfoxide, which is then oxidized to a sulfone, or hydroxylation to compounds that enter the carbon metabolic pool. |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | Not Available |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | Thiocarbamates are widely used throughout the world and are produced in great quantities, mainly as herbicides and fungicides.
|
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | Data concerning the effects of thiocarbamates on man are scarce. However, cases of irritation and sensitization have been observed among agricultural workers. Some thiocarbamates, e.g., molinate, have an effect on sperm morphology and, consequently, on reproduction. However, no teratogenic effects have been observed. The results of mutagenicity studies have shown that thiocarbamates containing dichloroallyl groups are highly mutagenic. Some thiocarbamates are acetylcholine esterase inhibitors. Acute exposure to cholinesterase inhibitors can cause a cholinergic crisis characterized by severe nausea/vomiting, salivation, sweating, bradycardia, hypotension, collapse, and convulsions. Increasing muscle weakness is a possibility and may result in death if respiratory muscles are involved. |
|---|
| Symptoms | As with organophosphates, the signs and symptoms are based on excessive cholinergic stimulation. Unlike organophosphate poisoning, carbamate poisonings tend to be of shorter duration because the inhibition of nervous tissue acetylcholinesterase is reversible, and carbamates are more rapidly metabolized. Muscle weakness, dizziness, sweating and slight body discomfort are commonly reported early symptoms. Headache, salivation, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain and diarrhea are often prominent at higher levels of exposure. Contraction of the pupils with blurred vision, incoordination, muscle twitching and slurred speech have been reported. (2) |
|---|
| Treatment | Treatment of carbamate poisoning is similar to that of organophosphate poisoning in that atropine sulfate injections readily reverse the effects. For acute exposures and first aid: EYES: irrigate opened eyes for several minutes under running water. INGESTION: do not induce vomiting. Rinse mouth with water (never give anything by mouth to an unconscious person). Seek immediate medical advice. SKIN: should be treated immediately by rinsing the affected parts in cold running water for at least 15 minutes, followed by thorough washing with soap and water. If necessary, the person should shower and change contaminated clothing and shoes, and then must seek medical attention. INHALATION: supply fresh air. If required provide artificial respiration.
|
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | Not Available |
|---|
| HMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 23675790 |
|---|
| ChEMBL ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChemSpider ID | 7844754 |
|---|
| KEGG ID | Not Available |
|---|
| UniProt ID | Not Available |
|---|
| OMIM ID | |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| CTD ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Stitch ID | Potassium asulam |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ACToR ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| MSDS | Not Available |
|---|
| General References | - IPCS Intox Database (1987). Antimony pentoxide. [Link]
- Fishel F (2009). Pesticide Toxicity Profile: Carbamate Pesticides. University of Florida, IFAS Extension. [Link]
|
|---|
| Gene Regulation |
|---|
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|