| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 2.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2009-06-17 23:53:04 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:23:00 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | T3D0980 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Mecarbinzid |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | Mecarbinzid is a systemic benzimidazole fungicide that is selectively toxic to microorganisms and invertebrates, especially earthworms. It is not widely used anymore due to widespread fungal resistance. The in vitro antifungal activity of benzimidazole compounds was first observed in 1944. Some of the benzimidazole derivatives which have been exploited for commercial use as agricultural pesticides are carbendazim, benomyl, mecarbinzid, debacarb, fuberidazole, and rabenzazole. Of these, carbendazim, benomyl, debacarb and mecarbinzid are benzimidazole-2-carbamates. benzimidazol-2-yl carbamates like Mecarbinzid bind to microtubules, interfering with cell functions, such as meiosis and intracellular transportation. Due to the widespread use of these fungicidal agents and their specific action, resistance is common in many fungal species. For instance, strains of Botrytis which cause gray mold in ornamental crops are now largely resistant to methyl benzimidazole carbamate fungicides. Solubility problems of these compounds have contributed to their low bioavailability which has restricted their use in the treatment of fungal diseases in plants and have now lost effectiveness for many important diseases. |
|---|
| Compound Type | - Carbamate
- Ether
- Lachrymator
- Organic Compound
- Pesticide
- Synthetic Compound
|
|---|
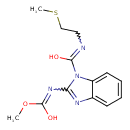
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | | Caswell No. 075A | | RCRA waste no. U271 |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C13H16N4O3S |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 308.356 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 308.094 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 27386-64-7 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | 2-{[hydroxy(methoxy)methylidene]amino}-N-[2-(methylsulfanyl)ethyl]-1H-1,3-benzodiazole-1-carboximidic acid |
|---|
| Traditional Name | 2-{[hydroxy(methoxy)methylidene]amino}-N-[2-(methylsulfanyl)ethyl]-1,3-benzodiazole-1-carboximidic acid |
|---|
| SMILES | COC(O)=NC1=NC2=CC=CC=C2N1C(O)=NCCSC |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C13H16N4O3S/c1-20-13(19)16-11-15-9-5-3-4-6-10(9)17(11)12(18)14-7-8-21-2/h3-6H,7-8H2,1-2H3,(H,14,18)(H,15,16,19) |
|---|
| InChI Key | InChIKey=ZCAHBOURBFRXOT-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as benzimidazoles. These are organic compounds containing a benzene ring fused to an imidazole ring (five member ring containing a nitrogen atom, 4 carbon atoms, and two double bonds). |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organoheterocyclic compounds |
|---|
| Class | Benzimidazoles |
|---|
| Sub Class | Not Available |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Benzimidazoles |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Benzimidazole
- N-substituted imidazole
- Benzenoid
- Azole
- Imidazole
- Heteroaromatic compound
- Isourea
- Carboximidic acid derivative
- Azacycle
- Thioether
- Sulfenyl compound
- Dialkylthioether
- Propargyl-type 1,3-dipolar organic compound
- Organic 1,3-dipolar compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Organooxygen compound
- Organosulfur compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organopnictogen compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Aromatic heteropolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Exogenous |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | Not Available |
|---|
| Applications | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Appearance | White powder. |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | | Solubility | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | View |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-052g-1983000000-0206c174767f47bca6d1 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-01qc-1900000000-85af49e091533582a74b | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-001i-1900000000-ee8f9ccc573b782fcc82 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-052g-7920000000-ab13c6ca7d3dd3df130e | 2016-08-04 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-0a6v-7890000000-e3b01249721c7e919ce2 | 2016-08-04 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-05ai-2900000000-51620d48bc343059a833 | 2016-08-04 | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Inhalation (2) ; oral (2); dermal (2) |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Mecarbinzid targets beta tubulin in actively dividing cells. It binds to microtubules, interfering with cell functions, such as meiosis and intracellular transportation (1). |
|---|
| Metabolism | The carbamates are hydrolyzed enzymatically by the liver; degradation products are excreted by the kidneys and the liver. (2) |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | Not Available |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | It is a systemic fungicide that is selectively toxic to microorganisms and invertebrates. It is also employed as a casting worm control agent in amenity turf situations such as golf greens and tennis courts. It is also used to control plant diseases in cereals and fruits, including citrus, bananas, strawberries, pineapples, and pomes. |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | The MRLs for fresh produce in the European Union are between 0.1 and 0.7 mg/kg
|
|---|
| Health Effects | Mecarbinzid is a suspected endocrine disruptor. It is also a developmental toxin. Animals exposed to Mecarbinzid in the womb to have serious deformities such as lack of eyes and hydrocephalus (water on the brain). Mecarbinzid can disrupt the development of sperm and damage testicular development in adult rats. |
|---|
| Symptoms | Skin redness and skin irritation. Fetuses exposed to high levels may exhibit microphthalmia (small eyes) or anaphthalmia (no eyes). |
|---|
| Treatment | For acute exposures and first aid: EYES: irrigate opened eyes for several minutes under running water. INGESTION: do not induce vomiting. Rinse mouth with water (never give anything by mouth to an unconscious person). Seek immediate medical advice. SKIN: should be treated immediately by rinsing the affected parts in cold running water for at least 15 minutes, followed by thorough washing with soap and water. If necessary, the person should shower and change contaminated clothing and shoes, and then must seek medical attention. INHALATION: supply fresh air. If required provide artificial respiration. |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | Not Available |
|---|
| HMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 20055210 |
|---|
| ChEMBL ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChemSpider ID | 16736373 |
|---|
| KEGG ID | C18942 |
|---|
| UniProt ID | Not Available |
|---|
| OMIM ID | |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 82083 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| CTD ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Stitch ID | Mecarbinzid |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ACToR ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| MSDS | Not Available |
|---|
| General References | - Clement MJ, Rathinasamy K, Adjadj E, Toma F, Curmi PA, Panda D: Benomyl and colchicine synergistically inhibit cell proliferation and mitosis: evidence of distinct binding sites for these agents in tubulin. Biochemistry. 2008 Dec 9;47(49):13016-25. doi: 10.1021/bi801136q. [19049291 ]
- IPCS Intox Database (1987). Antimony pentoxide. [Link]
- Fishel F (2009). Pesticide Toxicity Profile: Carbamate Pesticides. University of Florida, IFAS Extension. [Link]
|
|---|
| Gene Regulation |
|---|
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|